
In this method of sampling, the samples are created based on a certain set standard and they will have the same attributes as the entire population. Then the snowball sampling technique is used to collect data for the sample. The victims might not be open to discussing their situation with a researcher. For example, suppose a survey is conducted on the experiences of people with HIV or AIDS. This sampling technique is used when the study is based on a sensitive topic or the survey is very challenging.

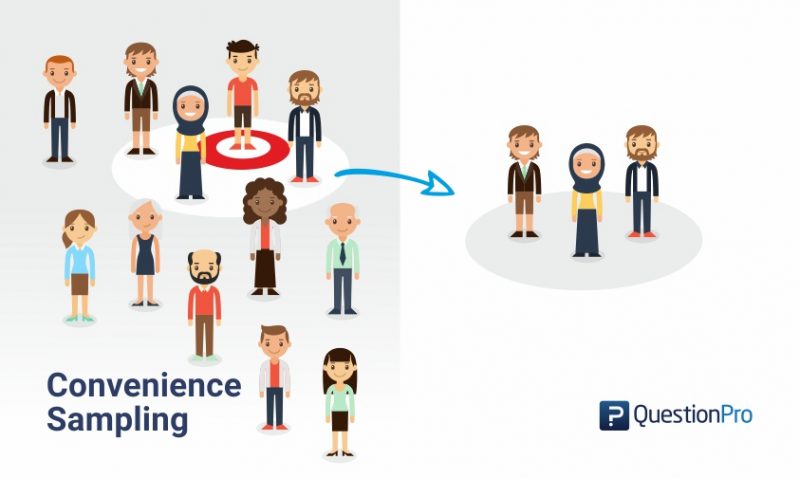
In such a case, they can either track a few categories to interview or they can recruit participants via other participants. Snowball sampling is a type of non-probability sampling in which the researchers do not have easy access to the subjects. To gather this data, she will purposefully only ask students who have disabilities about their experiences. For example, suppose a researcher wants to know the experiences of disabled students. This method of sampling is used when detailed knowledge of a particular phenomenon needs to be gathered. The target audience from which the sample is chosen is based on the discretion of the researcher. Judgemental or purposive sampling is used by researchers when they need to gather data for a very specific purpose. An example of this method of sampling is people standing at a mall and handing out flyers regarding a particular cause. However, the data gathered using this sampling technique may not be representative of the entire population. This method of sampling is used when initial data needs to be gathered in a cost-effective and inexpensive way. In other words, the entities that are easily accessible to the researcher form the sample. In convenience sampling, the collection of data from the subjects is dependent on their ease of access. The different types of non-probability sampling methods are as follows: Convenience Sampling The aim of this sampling method is to develop an initial understanding of the population.
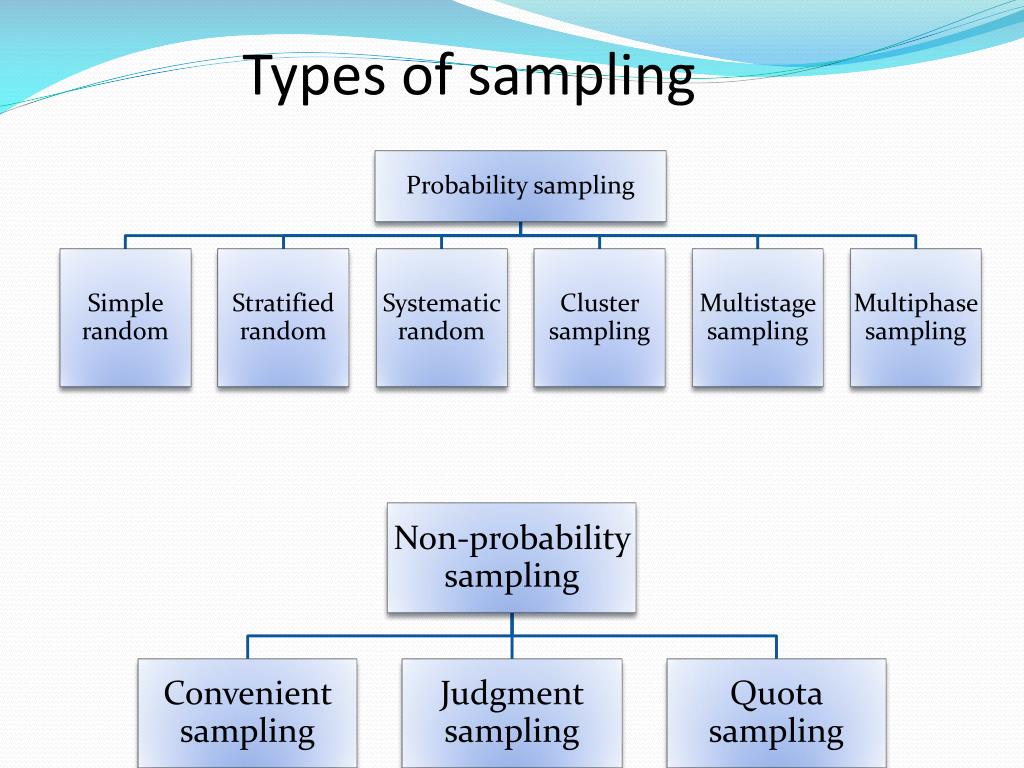
However, this method of sampling is more prone to sampling bias resulting in weaker conclusions drawn about the population. Non-probability sampling methods are used in qualitative research. This implies that not every entity has a chance of getting selected to be part of the sample. This method of sampling involves a non-random sampling technique wherein the samples are chosen based on certain criteria. Such a sampling technique is used for large populations, however, it is more prone to error as each cluster could possess substantial differences with respect to each other. The researcher then picks out any cluster to form the sample rather than choosing individuals at random. Each subgroup needs to have similar attributes to the whole sample. In this method of sampling, the researcher divides the entire population into subgroups known as clusters. Such a method of sampling ensures accurate representation of each subgroup. Then either simple or systematic random sampling is used to choose a sample from each subgroup separately. The researcher calculates how many entities need to be sampled from each subgroup on the basis of the proportions of the population. In stratified random sampling, the researcher divides the population into non-overlapping subgroups based on a particular characteristic. Such a sampling technique has a predefined range as well as a set starting point and the sampling size can be repeated at regular intervals. In systematic sampling, the entities of a population are assigned a number and the individuals are chosen at regular intervals.
#Random sampling techniques generator
Such a sampling technique can be conducted by using tools like a random number generator or any method that is based on only chance. A selection made using this sampling method is purely based on chance. When all the members of a population have an equally likely chance of being chosen it is known as the simple random sampling technique. The methods of sampling that fall under this category are as follows: Simple Random Sampling The aim of this sampling method is hypothesis testing. Probability sampling methods are used in quantitative research. In other words, each entity of such a population has an equal chance of getting selected to be part of the sample.
This method of sampling involves the random selection of any entity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
